But woe unto you, Pharisees! For ye tithe mint and rue and all manner of herbs, and pass over judgment and the love of God: these ought ye to have done, and not to leave the other undone.
By Kathryn Yateman
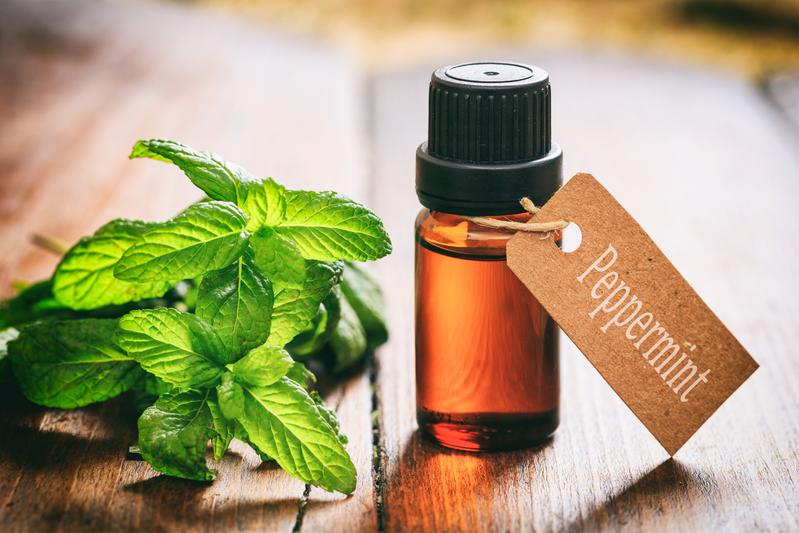
Did you know Peppermint is one of the oldest and most highly regarded herbs dating back to 1000 bc? Peppermint is thought to have originated in Northern Africa and the Mediterranean. In the Ebers Papyrus, an ancient Egyptian medical text dating to 1550 BC, mint is listed as calming to stomach pains. Mint was so valued in Egypt that it was used as a form of currency. In the Bible (Luke 11:39) Jesus tells the Pharisees:
In Greek mythology, Minthe was a river nymph in the Cocytus River (one of the five rivers of Hades). When Hades was driving his golden chariot, he came upon Minthe and was about to seduce her when his wife Persephone caught them. Persephone then turned Minthe into a lowly mint plant that people would walk upon. Mint supposedly got its pungent, sweet smell when Hades softened the spell so that when people walked upon his lover they would smell her sweetness. Peppermint gets the descriptor piperita from the particular peppery, pungency that distinguishes it from other members of the mint family.
The Roman natural philosopher Pliny wrote of mint and of peppermint in particular that it stimulated the appetite stirring “the mind and appetite to a greedy desire of food.” He also wrote that mint should be bound into a crown around the head in order to stimulate the mind and the soul. Pliny, Hippocrates and Aristotle all considered mint to be a discouragement to procreation, saying that it discouraged sexual intercourse. However, the Greeks said that mint encouraged sexual behavior and forbade its consumption by soldiers in order to maintain control.
Peppermint was eventually introduced to Europe where it also became a popular culinary and medicinal herb. It was mentioned in the Icelandic Pharmacopoeias as early as 1240 AD as an herbal remedy, and gained in popularity over the next two centuries. Monks in the Middle Ages were known to use peppermint as a tooth polisher and during the same period, cheese makers learned that the strong smell of peppermint would keep rats and mice out of the storeroom.
Peppermint appeared as a distinct species in the London Pharmacopoeia in 1721 and was listed as a remedy for treating all manner of ailments from sores, venereal disease, colds and headaches. As peppermint continued to gain in popularity the cultivation increased from just a few acres to several hundred acres.
When European settlers came to America they found that the American Indians were already aware of the importance of mint, though they were growing different species of mint, native to North America. The settlers brought peppermint and other non-native mints with them and they quickly became naturalized and spread.
In North America, peppermint is grown commercially almost exclusively in the north and east from Indiana to New York and the very southernmost areas of Canada. Michigan has the most acres under cultivation in the US, and altogether the US produces about half the world�s peppermint. However, American peppermint oil is considered much inferior to English oil, which is considered the best, followed by French peppermint oil. The difference is typically in the variety; in the US, the black variety is most often grown, while in Europe the more delicate white variety thrives.
Peppermint has been used for centuries to treat stomach upset and headaches. It has been used as a facial toner and as both a sexual stimulant and a sexual depressant. The most prominent beneficial ingredient in peppermint is menthol, but it also contains smaller amounts of menthone, cineol, rosmarinic acid, and limonene. Some new research confirms many health benefits of its use, including as a treatment for irritable bowel syndrome, as an antimicrobial, and even as a cancer fighting agent.Peppermint supplements can be taken fresh or dried, either whole or in capsules, in tea, in a tincture, or as an essential oil. The menthol in peppermint essential oil is very strong and may be irritating if used in large quantities without dilution. Oil in capsules is formulated with an enteric coating to prevent heartburn. When using essential oil it is often mixed in a glass of water or dropped onto a sugar cube.
In Ancient times, peppermint was used to calm and soothe dyspepsia, which eventually led to the traditional after dinner mint. Not only does an after dinner mint refresh the breath after eating strongly flavored dishes, it has been shown to relieve indigestion by calming the smooth muscles. This ability to relax the smooth muscles, such as those found around the stomach and intestines, are what make it effective in relieving the symptoms of IBS (irritable bowl syndrome). In a 2007 study, 78% of IBS sufferers got relief from cramping, constipation, bloating and diarrhea after taking peppermint oil capsules.
Even those without severe stomach troubles can benefit from a cup of peppermint tea after dinner to aid digestion. A drop of peppermint essential oil in a glass of water or dropped onto a cube of sugar can help prevent and relieve gas.
Researchers have also shown that peppermint oil can help increase the flow of bile. When taken with a fatty meal, it can help lessen symptoms for those with gall bladder disease.
Peppermint has both an analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. Peppermint oil is reputed to relieve the itching from insect bites, poison ivy, poison oak, and other itchy skin conditions. Peppermint oil in shampoos and conditioners can also help relieve an itchy scalp. The antimicrobial properties in peppermint kills germs on the skin without irritating the skin, helping to heal acne and other skin irritations. The menthol in peppermint essential oil can kill Salmonella, MRSA, and H. pylori.
Menthol is often used in toothpaste, and mint toothpaste is actually the most common variety. The menthol acts as a breath freshener and the germ killing action also fights bad breath.
Peppermint tea has long been thought to have a calming effect that can help to relieve stress and settle the mind before sleep. Just like menthol rub the menthol in mint tea can help to relieve congestion in the nose, throat and chest. Peppermint tea will also help soothe a cough. For best results with the tea, make a strong cup of peppermint tea and allow it to cool. Take sips every half an hour throughout the day, making more tea as needed. Menthol is also the main ingredient in many cough drops and cough syrups which relieve congestion.
To relieve headaches, mix 2 drops of peppermint essential oil in several drops of a mild carrier oil such as grapeseed oil or sweet almond oil. Rub this mixture on the temples or the pressure point behind the ears and rub it gently for several minutes.
Mint can also have a stimulating effect. A drop applied to the back of the tongue may give a mental boost and also help relieve sadness. Since ancient times, peppermint oil has been has been used to treat hysteria, shock, and stress.
Peppermint also contains high levels of vitamins and minerals including vitamin A, vitamin C, beta-carotene, and manganese. Vitamin C and carotenoids have both been shown helpful in preventing colon and rectal cancer.
Peppermint also contains high levels of the antioxidant rosmarinic acid. This antioxidant helps fight allergic asthma, atherosclerosis, and cancer. Rosmarinic acid has also been shown to help in treating cataracts, arthritis, and peptic ulcers.
Peppermint oil is an emmenagogue, meaning it stimulates menstruation. As such it can be helpful peppermint should be avoided in large quantities by pregnant women because of the chance of bringing on miscarriage. While peppermint oil is thought to be helpful in the treatment of dyspepsia and colic, use on infants should be limited because it can be irritating to the throat.
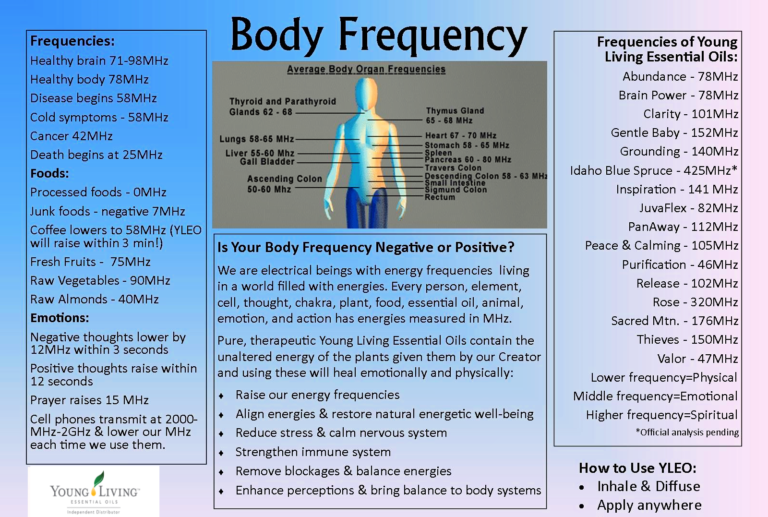
Free this month for Young Living members….oh yes please!
***Note***
This information is for educational purpose only and I am not here to treat diagnose or ….well you know 😁